|
I am currently a 5th-year Ph.D. student in the Intelligent Sensing, Perception and Computing (ISPC) Gruop led by Prof. Guang Chen at Tongji University, Shanghai, China, where I work on computer vision and machine learning. I received the M.Eng degree in Electronic and Communication Engineering from the National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, in 2018. I worked on FPGA logic programming and PCB design for my M.Eng. degree.
Email / CV / Bio / Google Scholar / Github |

|
|
I'm interested in computer vision, machine learning, multi-sensor fusion, and domain adaptation. Much of my research is about perceiving open, unknown visual domains using data or models from a single or several source domains (Closed-set Domain Adatpation, Open-set Domain Adaptation, Domain Generalization, Predictive Domain Adaptation). |
|
Representative papers are highlighted. |
|
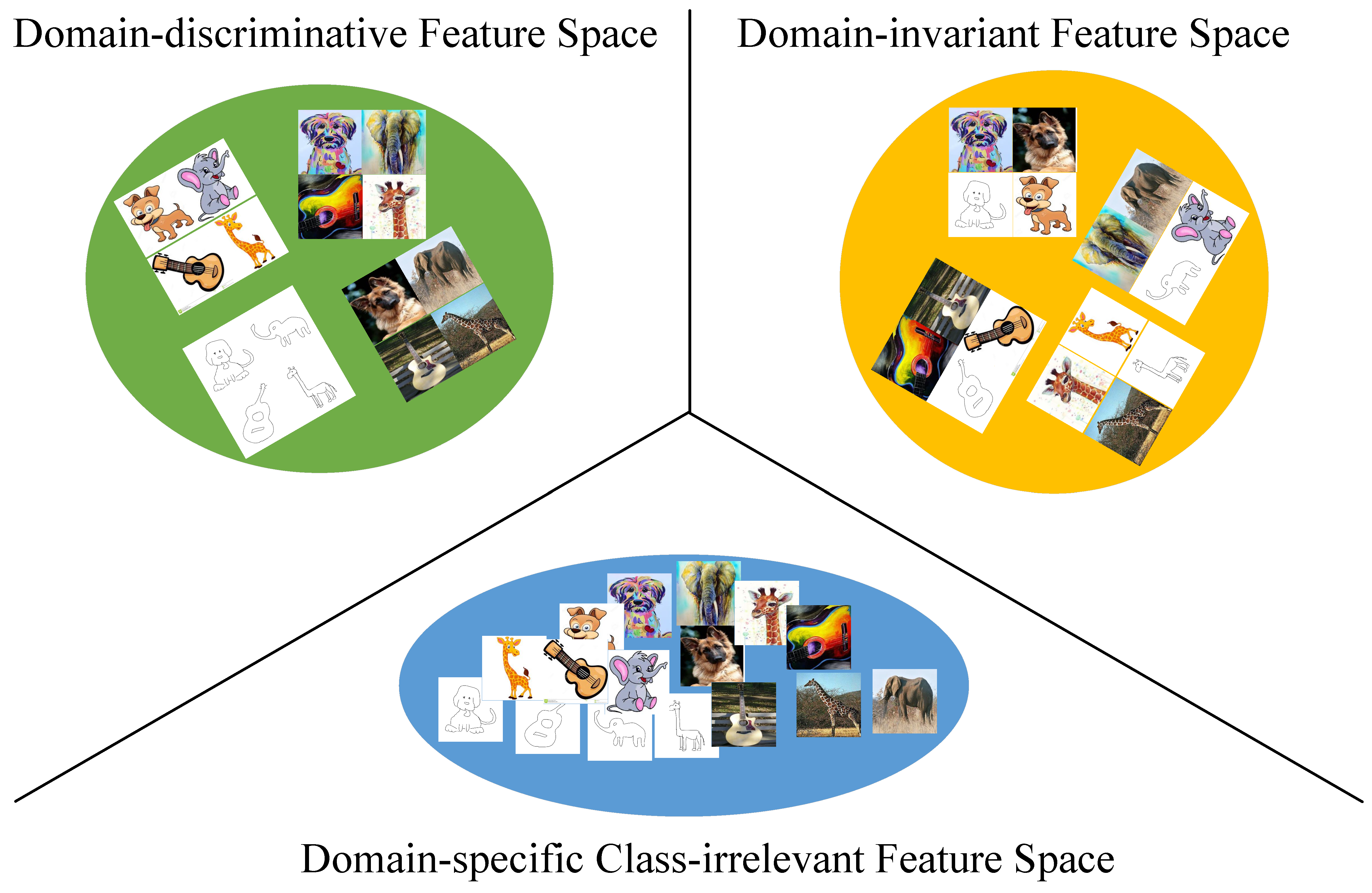
Zhengfa Liu, Guang Chen, Zhijun Li, Sanqing Qu, Yu Kang, Changjun Jiang IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2023 project page / video / arXiv Domain generalization (DG) aims to learn a model that generalizes well to an unseen test distribution. Mainstream methods follow the domain-invariant representational learning philosophy to achieve this goal. However, due to the lack of priori knowledge to determine which features are domain-specific and task-independent, and which features are domain-invariant and task-relevant, existing methods typically learn entangled representations, limiting their capacity to generalize to the distribution-shifted target domain. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose novel Disentangled Domain-Invariant Feature Learning Networks (D2IFLN), to adapt feature realize feature disentanglement and facilitate domain-invariant feature learning. |
|
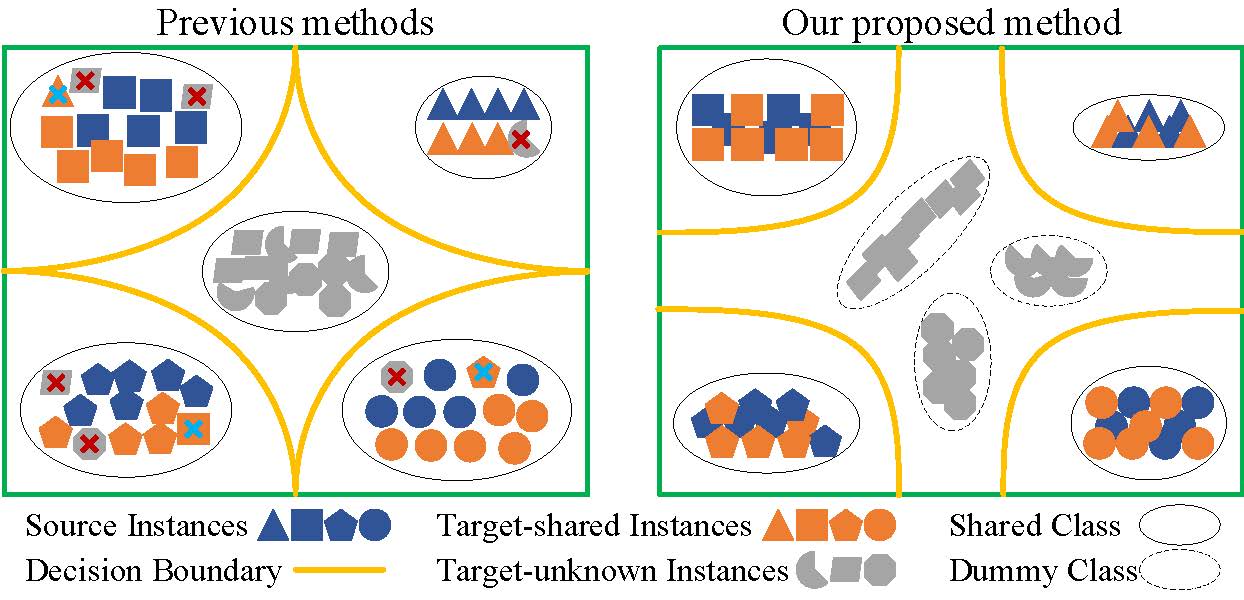
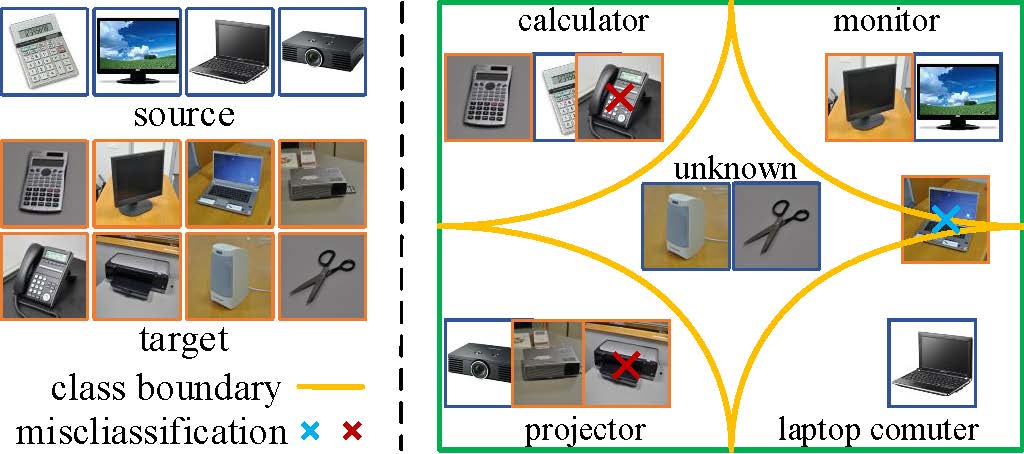
Zhengfa Liu, Guang Chen, Zhijun Li, Yu Kang, Sanqing Qu, Changjun Jiang IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022 project page / video / arXiv Open Set Domain Adaptation (OSDA) aims to achieve knowledge transfer in the presence of both domain shift and label shift, which assumes that there exist additional unknown target classes not presented in the source domain. To solve the OSDA problem, most existing methods introduce an additional unknown class to the source classifier and represent the unknown target instances as a whole. However, it is unreasonable to treat all unknown target instances as a group, since these unknown instances typically consist of distinct categories and distributions. It is challenging to identify all unknown instances with only one additional class. In addition, most existing methods directly introduce marginal distribution alignment to alleviate distribution shift between source and target domain, failing to learn discriminative class boundaries in the target domain since they ignore categorical discriminative information in the adaptation. To address these problems, in this paper, we propose a novel Prototype-based Shared-Dummy Classifier (PSDC) model for the OSDA. |
|
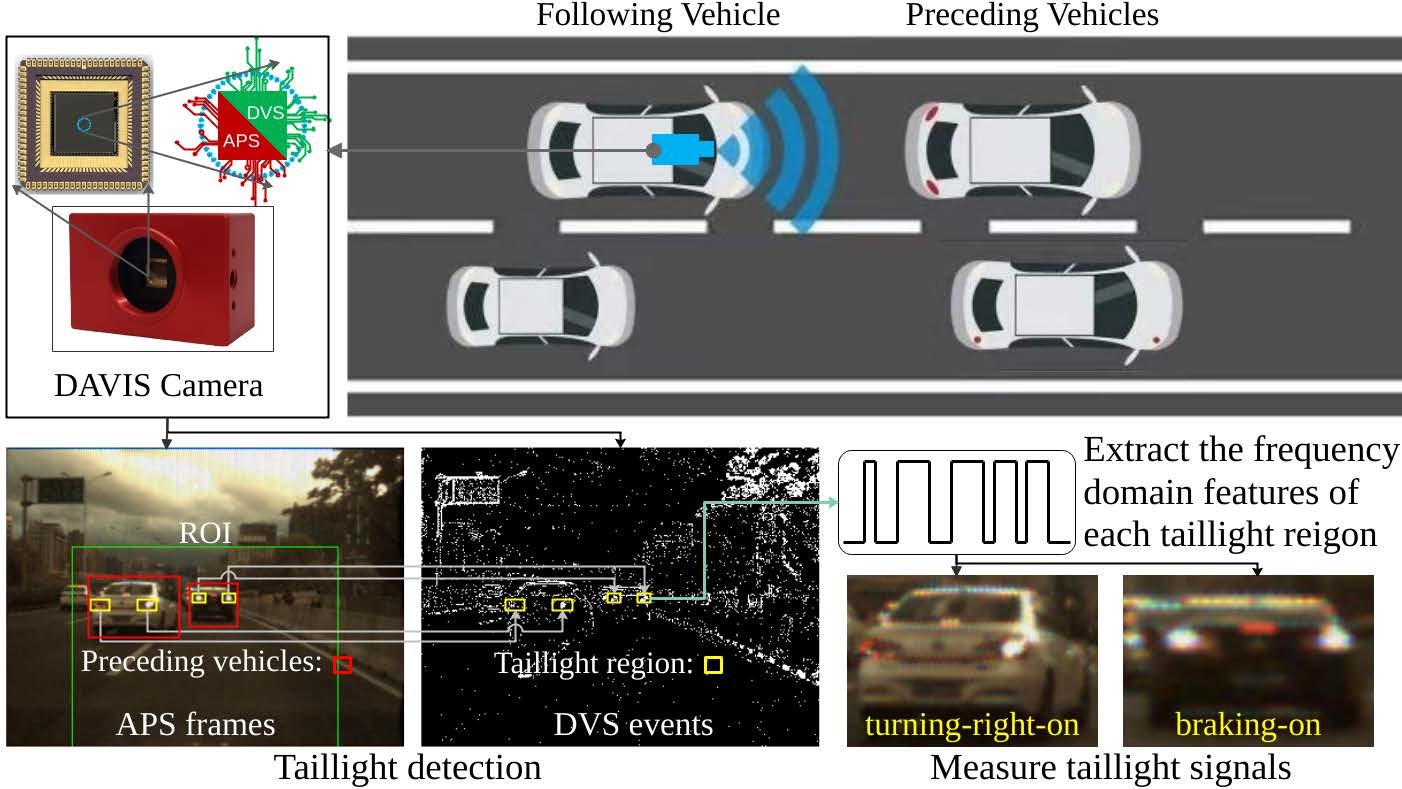
Zhengfa Liu, Guang Chen, Ya Wu, Jiatong Du, Jörg Conradt, Alois Knoll Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2022 project page / video / arXiv An important aspect of the perception system for intelligent vehicles is the detection and signal measurement of vehicle taillights. In this work, we present a novel vision-based measurement (VBM) system, using an event-based neuromorphic vision sensor, which is able to detect and measure the vehicle taillight signal robustly. To the best of our knowledge, it is for the first time the neuromorphic vision sensor is paid attention to for utilizing in the field of vehicle taillight signal measurement. In contrast to most existing work that relies purely on standard frame-based cameras for the taillight signal measurement, the presented mixed event/frame system extracts the frequency domain features from the spatial and temporal signal of each taillight region and measures the taillight signal by combining the active-pixel sensor (APS) frames and dynamic vision sensor (DVS) events. The results show the high potential of the event-based neuromorphic vision sensor being used for optical signal measurement applications, especially in dynamic environments. |
 
|
Guang Chen, Peigen Liu, Zhengfa Liu, Huajin Tang, Lin Hong, Jinhu Dong, Jörg Conradt, Alois Knoll IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020 project page / video / arXiv Abnormal event detection is an important task in research and industrial applications, which has received considerable attention in recent years. Existing methods usually rely on standard frame-based cameras to record the data and process them with computer vision technologies. In contrast, this paper presents a novel neuromorphic vision based abnormal event detection system. Compared to the frame-based camera, neuromorphic vision sensors, such as Dynamic Vision Sensor (DVS), do not acquire full images at a fixed frame rate but rather have independent pixels that output intensity changes (called events) asynchronously at the time they occur. Thus, it avoids the design of the encryption scheme. Additionally, we build the NeuroAED dataset, the first public dataset dedicated to abnormal event detection with neuromorphic vision sensor. The NeuroAED dataset consists of four sub-datasets: Walking, Campus, Square, and Stair dataset. |